Hydrology+#
Summary#
Hydrology+ is a powerful new feature as of version 7 of Flood Modeller which integrates the industry-standard WINFAP and ReFH2 hydrological packages with Flood Modeller, introducing enhanced flexibility and time-savings for both hydrologists and hydraulic modellers.
For more information on Hydrology+ go to: floodmodeller.com/hydrologyplus
Whilst the majority of hydrological analysis can be done within the Flood Modeller interface, the
Flood Modeller API offers integration with Hydrology+ through the floodmodeller_api.hydrology_plus
module in 3 ways:
Support for exported flow data from Hydrology+ using the
HydrologyPlusExportclassSupport for quickly generating sets of IEF files based on exported flow data
[Not yet available] Direct connection to the Hydrology+ database for advanced analysis (power users only)
Hydrology+ exported flow data#
Once hydrological analysis has been undertaken in Flood Modeller, the resultant flow data can be exported into csv format, containing metadata as well as flow data for a combination of different return periods, storm durations and scenarios.
These exported csv files can be read using the API class HydrologyPlusExport
or using the helper functions load_hydrology_plus_csv_export() or read_file():
In [1]: from floodmodeller_api.hydrology_plus import load_hydrology_plus_csv_export, HydrologyPlusExport;
In [2]: from floodmodeller_api import read_file;
In [3]: HydrologyPlusExport("example_h+_export.csv"); # Load using class directly
In [4]: load_hydrology_plus_csv_export("example_h+_export.csv"); # Load using H+ helper function
In [5]: read_file("example_h+_export.csv"); # Load using main API helper function
Once loaded, the HydrologyPlusExport class can access the metadata and flow data.
In [6]: hplus = HydrologyPlusExport("example_h+_export.csv")
In [7]: hplus.metadata
Out[7]:
{'Hydrograph Name': 'Baseline unchecked',
'Hydrograph Description': '',
'Calculation Point': 'CP_003',
'ReFH2 Name': 'CP_003_ReFH2_1',
'Winfap Name': 'CP_003_WINFAP_1',
'Urban/Rural': 'Urban',
'Urban/Rural Comment': '',
'ReFH2 Comment': '',
'Winfap Comment': '',
'Winfap Distribution': 'GEV',
'Winfap Distribution Comment': '',
'Use Climate Change Allowances': 'True',
'Use Custom Scale Factors': 'False',
'Created By': 'KA007155',
'Created Date': '30/04/2024 09:42:23',
'Checksum': 'ef77d9bd-2eb3-4689-a1e3-665d293db810'}
In [8]: hplus.return_periods
Out[8]: [1.0, 2.0, 5.0, 10.0, 30.0, 50.0, 75.0, 100.0, 200.0, 1000.0]
In [9]: hplus.storm_durations
Out[9]: [11.0]
In [10]: hplus.scenarios
Out[10]: ['2020 Upper', 'Reconciled Baseline']
In [11]: hplus.data.head()
Out[11]:
Reconciled Baseline - 11 - 1 - Flow (m3/s) ... 2020 Upper - 11 - 1000 - Flow (m3/s)
Time (hours) ...
0 1.341 ... 1.417
1 1.325 ... 1.439
2 1.338 ... 1.599
3 1.403 ... 1.997
4 1.554 ... 2.808
[5 rows x 20 columns]
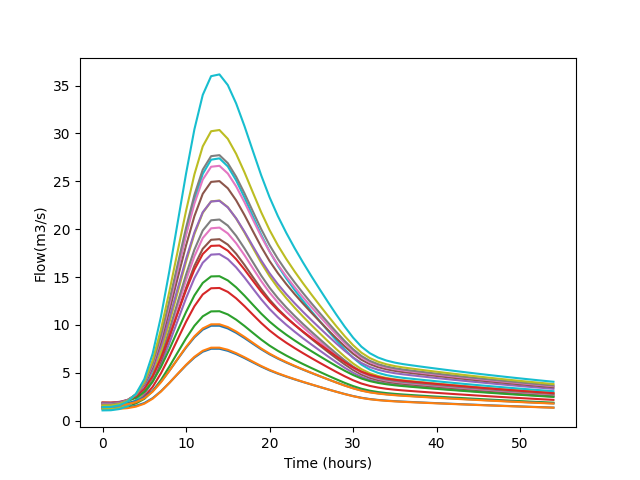
In [12]: hplus.data.plot(ylabel="Flow(m3/s)", legend=False);
You can also access specific event flow data by either passing in the full event string or the
individual components in the get_event_flow() method:
In [13]: event_flow = hplus.get_event_flow(
....: scenario="2020 Upper",
....: storm_duration=11.0,
....: return_period=100,
....: )
....:
In [14]: event_flow
Out[14]:
Time (hours)
0 1.679
1 1.685
2 1.803
3 2.111
4 2.742
5 3.929
6 5.980
7 8.941
8 12.511
9 16.344
10 20.144
11 23.577
12 26.216
13 27.627
14 27.733
15 26.897
16 25.482
17 23.745
18 21.862
19 20.004
20 18.336
21 16.895
22 15.619
23 14.444
24 13.336
25 12.278
26 11.252
27 10.244
28 9.262
29 8.325
30 7.471
31 6.763
32 6.252
33 5.901
34 5.657
35 5.479
36 5.343
37 5.231
38 5.125
39 5.020
40 4.916
41 4.816
42 4.717
43 4.619
44 4.525
45 4.431
46 4.341
47 4.252
48 4.165
49 4.079
50 3.996
51 3.913
52 3.833
53 3.754
54 3.677
Name: 2020 Upper - 11 - 100 - Flow (m3/s), dtype: float64
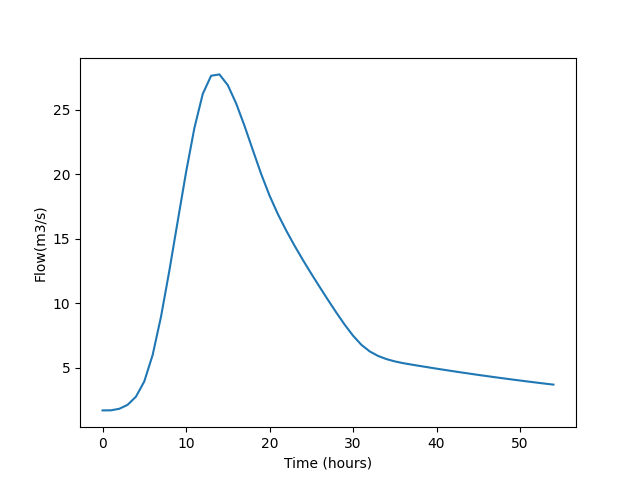
In [15]: event_flow.plot(ylabel="Flow(m3/s)");
A similar option is available to return a single event flow as a QTBDY unit. For example, to extract
a QTBDY and add into a new IED file we use the get_qtbdy() method:
In [16]: from floodmodeller_api import IED;
In [17]: from floodmodeller_api.units import QTBDY;
In [18]: qtbdy = hplus.get_qtbdy(
....: qtbdy_name="New_QT001",
....: scenario="2020 Upper",
....: storm_duration=11.0,
....: return_period=100,
....: )
....:
In [19]: new_ied = IED();
In [20]: new_ied.boundaries[qtbdy.name] = qtbdy;
In [21]: print(new_ied._write())
QTBDY
New_QT001
55 0.000 0.000 HOURS EXTEND LINEAR 0.000 0.000 OVERRIDE
1.679 0
1.685 1
1.803 2
2.111 3
2.742 4
3.929 5
5.980 6
8.941 7
12.511 8
16.344 9
20.144 10
23.577 11
26.216 12
27.627 13
27.733 14
26.897 15
25.482 16
23.745 17
21.862 18
20.004 19
18.336 20
16.895 21
15.619 22
14.444 23
13.336 24
12.278 25
11.252 26
10.244 27
9.262 28
8.325 29
7.471 30
6.763 31
6.252 32
5.901 33
5.657 34
5.479 35
5.343 36
5.231 37
5.125 38
5.020 39
4.916 40
4.816 41
4.717 42
4.619 43
4.525 44
4.431 45
4.341 46
4.252 47
4.165 48
4.079 49
3.996 50
3.913 51
3.833 52
3.754 53
3.677 54
Generating IEF data#
With the HydrologyPlusExport class instantiated, we can generate
IEF files with flowtimeprofiles based on the data in the CSV. This can be done based on a blank IEF
with no other attributes set, or based on a given template IEF. We can generate a full set of IEF files
using the generate_iefs() method, or a
single ief using generate_ief():
In [22]: ief = hplus.generate_ief(node_label="INFLOW_001", event="2020 Upper - 11 - 100");
In [23]: ief
Out[23]: <floodmodeller_api Class: IEF(filepath=2020Upper-11-100_generated.ief)>
In [24]: print(ief._write())
[ISIS Event Header]
Title=
Datafile=
Results=
[ISIS Event Details]
RunType=Steady
Start=0
ICsFrom=1
[Flow Time Profiles]
NoOfFlowTimeProfiles=1
NoOfFlowTimeSeries=1
FlowTimeProfile0=INFLOW_001,19,23,example_h+_export.csv,hplus,2020 Upper - 11 - 100 - Flow (m3/s),Generated by HydrologyPlusExport
In [25]: iefs = hplus.generate_iefs(node_label="INFLOW_001");
In [26]: for ief in iefs:
....: print(ief)
....:
<floodmodeller_api Class: IEF(filepath=ReconciledBaseline-11-1_generated.ief)>
<floodmodeller_api Class: IEF(filepath=ReconciledBaseline-11-2_generated.ief)>
<floodmodeller_api Class: IEF(filepath=ReconciledBaseline-11-5_generated.ief)>
<floodmodeller_api Class: IEF(filepath=ReconciledBaseline-11-10_generated.ief)>
<floodmodeller_api Class: IEF(filepath=ReconciledBaseline-11-30_generated.ief)>
<floodmodeller_api Class: IEF(filepath=ReconciledBaseline-11-50_generated.ief)>
<floodmodeller_api Class: IEF(filepath=ReconciledBaseline-11-75_generated.ief)>
<floodmodeller_api Class: IEF(filepath=ReconciledBaseline-11-100_generated.ief)>
<floodmodeller_api Class: IEF(filepath=ReconciledBaseline-11-200_generated.ief)>
<floodmodeller_api Class: IEF(filepath=ReconciledBaseline-11-1000_generated.ief)>
<floodmodeller_api Class: IEF(filepath=2020Upper-11-1_generated.ief)>
<floodmodeller_api Class: IEF(filepath=2020Upper-11-2_generated.ief)>
<floodmodeller_api Class: IEF(filepath=2020Upper-11-5_generated.ief)>
<floodmodeller_api Class: IEF(filepath=2020Upper-11-10_generated.ief)>
<floodmodeller_api Class: IEF(filepath=2020Upper-11-30_generated.ief)>
<floodmodeller_api Class: IEF(filepath=2020Upper-11-50_generated.ief)>
<floodmodeller_api Class: IEF(filepath=2020Upper-11-75_generated.ief)>
<floodmodeller_api Class: IEF(filepath=2020Upper-11-100_generated.ief)>
<floodmodeller_api Class: IEF(filepath=2020Upper-11-200_generated.ief)>
<floodmodeller_api Class: IEF(filepath=2020Upper-11-1000_generated.ief)>
Reference#
- class floodmodeller_api.hydrology_plus.HydrologyPlusExport(csv_file_path: str | Path, from_json: bool = False)#
Class to handle the exported output of Hydrology +
- Parameters:
csv_file_path (str | Path) – produced by Hydrology + in Flood Modeller
- Output:
Initiates ‘HydrologyPlusExport’ object The event/s needed to run simulations in Flood Modeller
- property data: DataFrame#
Hydrograph flow data for all events as a pandas DataFrame.
- property metadata: dict[str, str]#
Metadata associated with Hydrology+ csv export.
- property return_periods: list#
Distinct return periods from exported Hydrology+ data
- property storm_durations: list#
Distinct storm durations from exported Hydrology+ data
- property scenarios: list#
Distinct scenarios from exported Hydrology+ data
- generate_ief(node_label: str, template_ief: IEF | Path | str | None = None, event: str | None = None, return_period: float | None = None, storm_duration: float | None = None, scenario: str | None = None) IEF#
Generates a single IEF file for the requested event.
The IEF file is saved to disk in the same location as the Hydrology+ Export file and is named with the pattern {profile name}_generated.ief. The IEF instance is also returned for further editing/saving if desired.
- Parameters:
node_label (str) – Node label in model network to associate flow data with.
template_ief (IEF | Path | str | None, optional) – A template IEF instance, a file path, or a string representing the path to an IEF. If not provided, a new blank IEF instance is created.
event (str, optional) – Full string identifier for the event in the dataset. If provided, this takes precedence over other parameters.
return_period (float, optional) – The return period of the event.
storm_duration (float, optional) – The duration of the storm event in hours.
scenario (str, optional) – The scenario name, which typically relates to different conditions (e.g., climate change scenario).
- Returns:
An IEF instance.
- Return type:
- generate_iefs(node_label: str, template_ief: IEF | Path | str | None = None) list[IEF]#
Generates a set of IEF files for all available events in the Hydrology+ Export file.
The IEF files are saved to disk in the same location as the Hydrology+ Export file and are named with the pattern {profile name}_generated.ief. They are also returned as a list of IEF instances for further editing/saving if desired.
- Parameters:
node_label (str) – Node label in model network to associate flow data with.
template_ief (IEF | Path | str | None, optional) – A template IEF instance, a file path, or a string representing the path to an IEF. If not provided, a new blank IEF instance is created.
- Returns:
A list of IEF instances, one for each event.
- Return type:
list[IEF]
- get_event_flow(event: str | None = None, return_period: float | None = None, storm_duration: float | None = None, scenario: str | None = None) Series#
Extracts a specific event’s flow data from the exported Hydrology+ flow data.
- Parameters:
event (str, optional) – Full string identifier for the event in the dataset. If provided, this takes precedence over other parameters.
return_period (float, optional) – The return period of the event.
storm_duration (float, optional) – The duration of the storm event in hours.
scenario (str, optional) – The scenario name, which typically relates to different conditions (e.g., climate change scenario).
- Returns:
A pandas Series containing the flow data (m³/s) for the specified event.
- Return type:
pd.Series
- Raises:
FloodModellerAPIError – If the csv file is not in the correct format.
ValueError – If the event arg is not provided and one or more of return_period, storm_duration, or scenario is missing.
ValueError – If no matching event is found in the dataset.
Note
If the event parameter is provided, the method returns the data corresponding to that event.
If event is not provided, the method attempts to locate the event based on the combination of return_period, storm_duration, and scenario.
The dataset is assumed to have columns named in the format “scenario - storm_duration - return_period - Flow (m3/s)”.
- get_flowtimeprofile(node_label: str, event: str | None = None, return_period: float | None = None, storm_duration: float | None = None, scenario: str | None = None) FlowTimeProfile#
Generates a FlowTimeProfile object based on the requested event.
- Parameters:
node_label (str) – Node label in model network to associate flow data with.
event (str, optional) – Full string identifier for the event in the dataset. If provided, this takes precedence over other parameters.
return_period (float, optional) – The return period of the event.
storm_duration (float, optional) – The duration of the storm event in hours.
scenario (str, optional) – The scenario name, which typically relates to different conditions (e.g., climate change scenario).
- Returns:
A FlowTimeProfile object containing the attributes required for an IEF.
- Return type:
- Raises:
FloodModellerAPIError – If the csv file is not in the correct format.
ValueError – If the event arg is not provided and one or more of return_period, storm_duration, or scenario is missing.
ValueError – If no matching event is found in the dataset.
Note
If the event parameter is provided, the method returns the data corresponding to that event.
If event is not provided, the method attempts to locate the event based on the combination of return_period, storm_duration, and scenario.
The dataset is assumed to have columns named in the format “scenario - storm_duration - return_period - Flow (m3/s)”.
- get_qtbdy(qtbdy_name: str | None, event: str | None = None, return_period: float | None = None, storm_duration: float | None = None, scenario: str | None = None, **kwargs) QTBDY#
Generates a QTBDY unit based on the flow time series of the requested event.
- Parameters:
qtbdy_name (str, optional) – Name of the new QTBDY unit. If not provided a default name is used.
event (str, optional) – Full string identifier for the event in the dataset. If provided, this takes precedence over other parameters.
return_period (float, optional) – The return period of the event.
storm_duration (float, optional) – The duration of the storm event in hours.
scenario (str, optional) – The scenario name, which typically relates to different conditions (e.g., climate change scenario).
**kwargs – Additional keyword args can be passed to build the QTBDY unit. See
QTBDYfor details.
- Returns:
A QTBDY object containing the flow data (m³/s) for the specified event.
- Return type:
- Raises:
FloodModellerAPIError – If the csv file is not in the correct format.
ValueError – If the event arg is not provided and one or more of return_period, storm_duration, or scenario is missing.
ValueError – If no matching event is found in the dataset.
Note
If the event parameter is provided, the method returns the data corresponding to that event.
If event is not provided, the method attempts to locate the event based on the combination of return_period, storm_duration, and scenario.
The dataset is assumed to have columns named in the format “scenario - storm_duration - return_period - Flow (m3/s)”.
